The ultimate guide to compression: our best tips and step-by-step guides
We dissect the don of dynamics processors

Compress to impress
Whether you're beefing up a kick or mastering an entire track, it's all about dynamics processing, and compression is at its heart.
Compression will always be the subject of heated debate in regard to appropriate usage (don't mention the Loudness War...), but whether you like to use liberal amounts of it all over your mixes, prefer to apply it in small doses, or just want to learn more about the subject, we can help.
Click through the gallery to find links to some of MusicRadar's most popular compression-related articles. Whether you want to find out more about serial and parallel compression, learn how to master from the pros, discover how to nail sidechain compression, or even build a modular compressor, the knowledge you need is right here.

How to add body with parallel compression
Parallel - or 'New York style' - compression is excellent for adding density to a sound while retaining transient response in a way that normal compression doesn't.
The technique involves using a (usually, but not always) hyper-compressed version of the signal mixed with the original dry feed, allowing average volume to be increased without compromising the transient snap of the original sound. It can be done by using any compressor on a send/return channel, or a compressor equipped with a wet/dry control directly on the sound's channel itself.
READ: How to add body with parallel compression
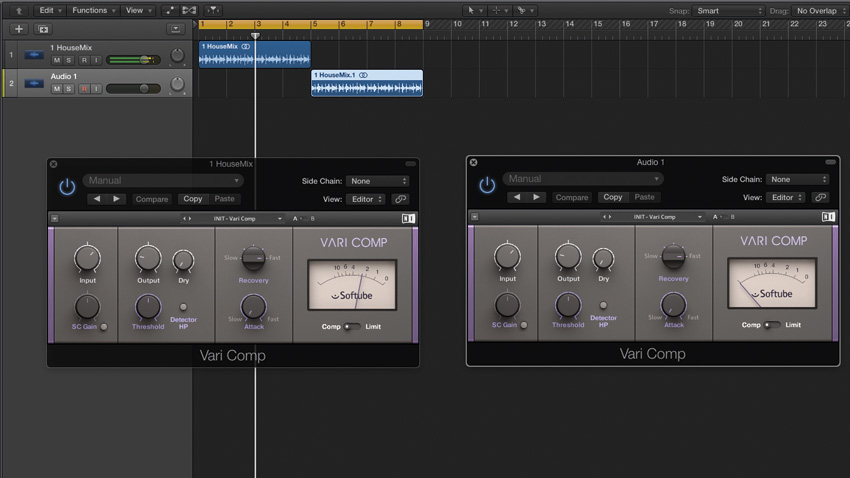
How to use serial compression
Serial compression means using multiple compressors in series (ie, one after the other), and it's a great way to combine the most desirable attributes and/or capabilities of two or more plugins.
A practical example would be using a slow acting compressor such as Native Instruments' Vari Comp, which is modelled on a classic valve design, followed by a more modern compressor like an SSL clone or digital compressor with lookahead. By using two complementary units together like this, it's possible to harness the general levelling behaviour and vibe of the first alongside the clinical peak control and clean sound of the second - great for recreating the feel of outboard gear 'in the box' while retaining the precision that modern processors are known for.
READ: How to use serial compression
13 advanced compression features explained
The basics of compression aren't that hard to grasp: simply set a threshold above which the input signal is reduced in volume to an extent specified by the ratio control, with the speed of that reduction and its subsequent recovery determined by the attack and release parameters.
However, there's much more to dynamic signal leveling than just that, and in this feature we'll show you 13 more esoteric compression features - control over most or all of which should be offered by any serious compressor plugin - that can be exploited to fine-tune, finesse and generally tailor the process.
READ: 13 advanced compression features explained

Master bus compression explained... by a mastering engineer
Master bus compression is used both when mixing and mastering tracks, but with so many compressor options available in plugin form - including a host of classics such as the SSL Bus Compressor, API 2500 and Neve 33609 - the temptation is to go full-tilt in search of that elusive mix 'glue' you'll have heard mentioned. But tread carefully, as bad compression on your master mix can't be undone, and an eagerly set-up mix compressor may well end up hiding poor balance decisions as your mix progresses.
To get some clarity on the matter and an overview on other master dynamics processors such as limiters and multiband processors, we chatted to mastering engineer Doug Shearer. With an eclectic credit list (Guillemots, Gorillaz, Coldplay, Patrick Wolf, The Fall) and time at a number of the UK's top facilities, his vinyl cutting experience sees him currently working at Andy Parnell's Black Saloon Studios.
READ: Master bus compression explained... by a mastering engineer
How to control mix elements with mid/side compression
Mid/side compression is a technique used by many pro engineers for increased flexibility when processing stereo material. By encoding a stereo signal from L/R to M/S, it's possible to compress the mono (mid) and stereo (side) elements of the signal independently. Why would we want to do this, though?
Typically, a full mix or dense stereo stem will carry most of its energy in the centre of the stereo field, meaning that when stereo compression is applied, the whole stereo image is affected as the compressor acts upon the loudest parts of the signal. Using a mid/side compressor enables us to apply differing amounts of compression to the mid and side channels - ideal for compressing an overly loud kick drum in the centre of the stereo field without overly affecting a far wider overheads track with crashes on it, for example.
READ: How to control mix elements with mid/side compression
How to control mixed material with multiband compression
Multiband compression is a powerful tool that offers incredibly flexible control over a signal's dynamics. Whereas conventional compression acts on the entire frequency range of a signal, a multiband device allows the user to compress discrete frequency bands individually.
Let's use a three-band compressor as a basic example of how it works: the incoming signal is split across these bands by adjustable low-pass, band-pass and high-pass filters, similar to those used by a PA system crossover. The signals are routed to individual compressors for tailored processing, before being recombined into one signal again.
READ: How to control mixed material with multiband compression
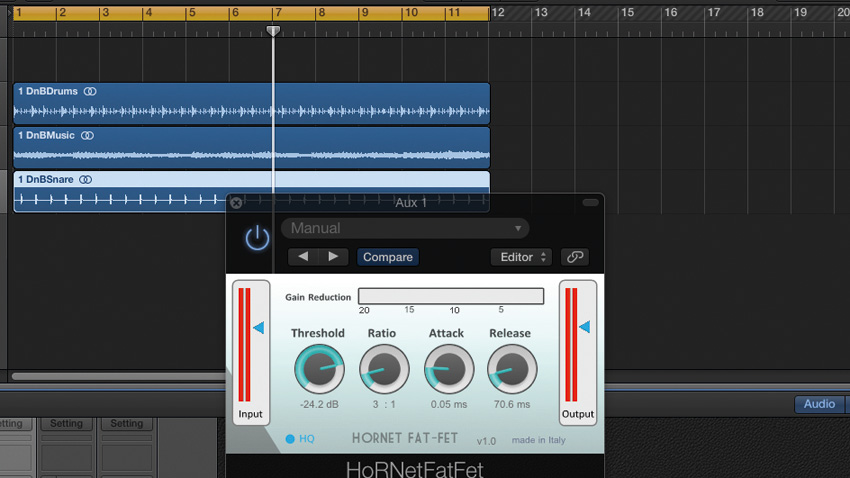
How to make specific drums 'pop' with reverse parallel compression
When your drum bus compression is working well overall, but one or more elements of the kit are suffering a bit in terms of snap and transient because of it, this technique can save your bacon.
By sending individual sounds to a return channel in parallel with the compressed bus, each one can be mixed back in in its uncompressed form to bring the attack of that particular sound out. Read on to find out how it's done…
READ: How to make specific drums 'pop' with reverse parallel compression

How to use New York compression on drums
The New York compression technique is particularly effective on beats, as it allows the initial transients and power of dry drum sounds to be enhanced with a squashed but dynamically more consistent second audio signal that can be blended in under the original parts.
In this tutorial we've started with a typical combination of elements, which combine to form a loop. They work well together but lack power. So, they're then routed to an auxiliary ready for a parallel compression treatment.
Don't send so much signal from each track that the auxiliary channel is overloading - introducing distortion by accident won't help your tracks. Then, add the stereo compressor of your choice. A high ratio, coupled to a low threshold (to ensure the whole buss is compressing hard) is a good start, but play with attack and release times too…
READ: How to use New York compression on drums
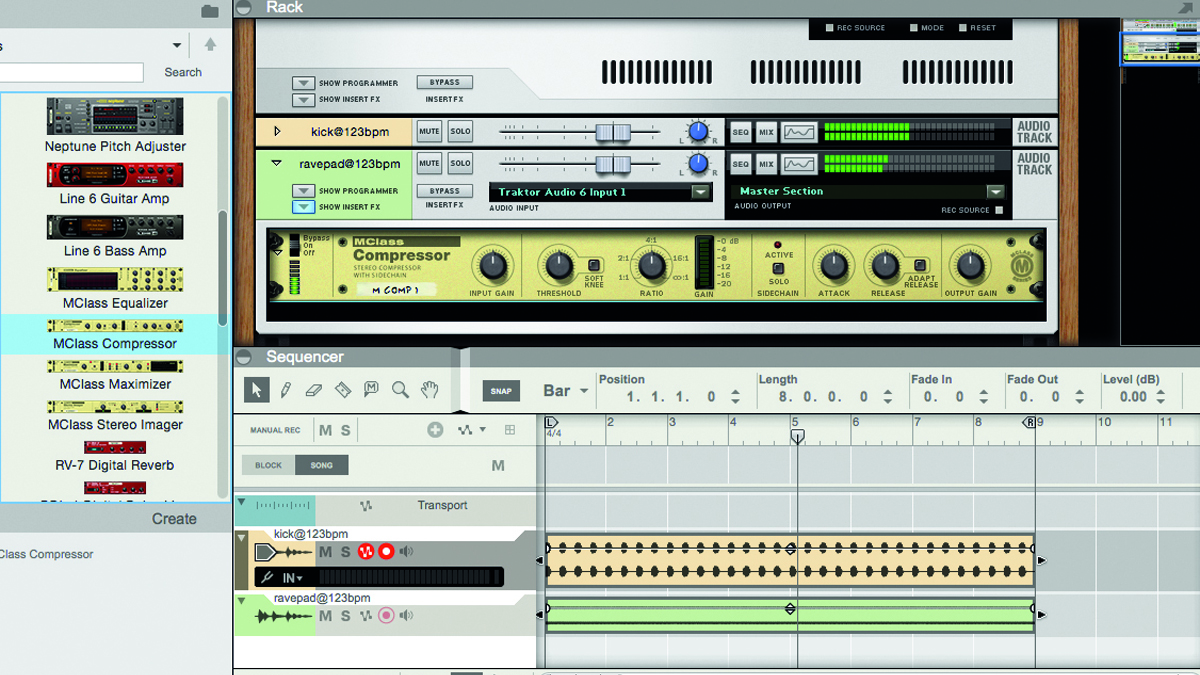
How to create classic pumping sidechain compression
If we had to choose one production technique that we reckon has had more profound an effect than any other on the sound of dance music in the 21st century, it would undoubtedly be sidechain compression.
Ever since some bright spark first strapped a compressor over their bass bus and fed a 4/4 kick drum into its external key input, producers the world over have been mad for overt sidechaining. Indeed, it's highly likely you already use it as a matter of course. If, however, you've yet to give it a try, this walkthrough is for you…
READ: How to create classic pumping sidechain compression
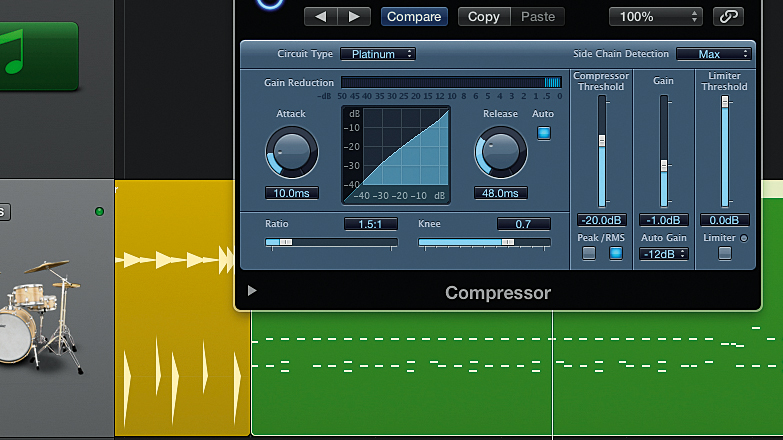
How to beef-up drums with snap compression
Dynamics processors are on of the most important tools in any producer's toolbox, yet they're not especially intuitive, and many producers struggle to understand how they really work, which sometimes results in them doing more harm than good to their mixes.
What you need, then, is a solid grounding in the fundamentals of how these vital mix tools work, of the scientific-sounding terminology that goes along with them, and the tried-and-tested techniques and starting points that'll allow you to use them with confidence.
READ: How to beef-up drums with snap compression
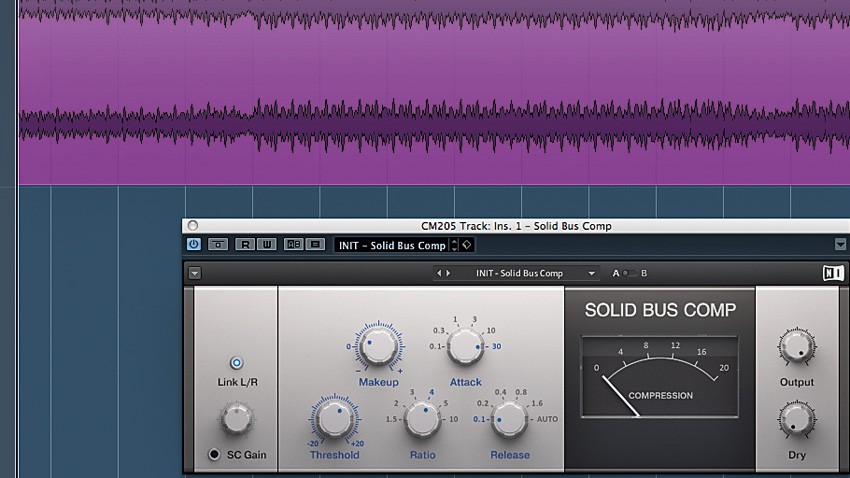
How to 'gel' a mix with master bus compression
Master bus compression - quite simply, the use of a compressor on the master or mix bus - can make a profound difference to the overall sonic quality of a mix, binding its individual components together into a cohesive, professional-sounding whole.
With great power, though, comes great responsibility, and if you don't fully understand what you're doing with the controls of your compressor, you can do considerably more harm than good. With that in mind, here's a quick guide to get you started.
READ: How to 'gel' a mix with master bus compression
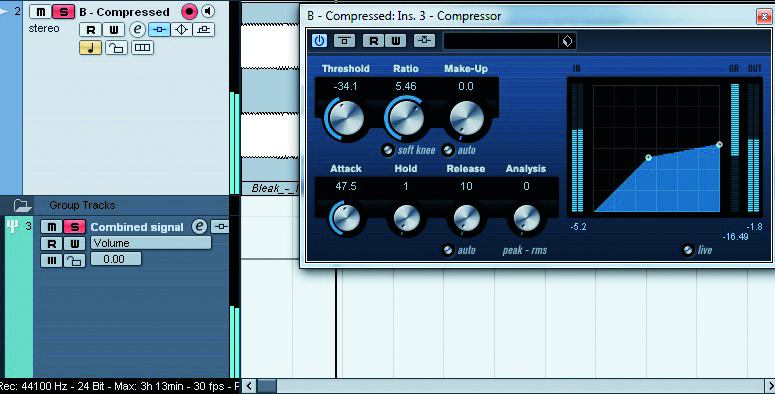
Understanding parallel compression
Parallel processing is a powerful weapon used by many mastering engineers. This process involves duplicating the signal, i.e. having two versions of the same song (let's call them 'A' and 'B'), and then very heavily compressing signal B while leaving signal A untouched by compression.
As a result you turn the negative implications of compression around into upward expansion. Signal A's dynamic range remains entirely untouched, which is great, and it becomes complemented by the heavily squashed signal B, which can really 'beef-up' the overall impact of the song. It's kind of like having an ugly wingman to make you look good.Signal B is only there to compliment signal A and so not much of signal B is needed to have a nice effect.
READ: Understanding parallel compression
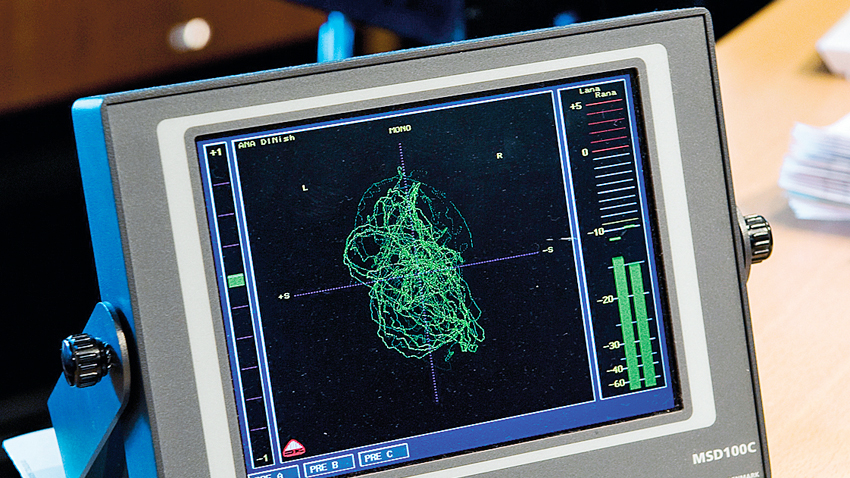
Understanding dynamic range and compression
In this video tutorial you will hear Conor Dalton, a mastering engineer who runs Glowcast Audio Mastering, explain dynamic range and compression.
READ: Understanding dynamic range and compression
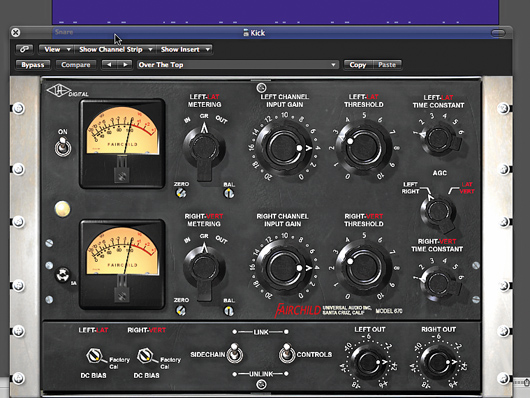
How to make fat compressed beats
How come some records’ beats sound so much fatter than others? Well, it’s got a lot to do with the original sounds chosen for the backing tracks, but more crucially, it’s down to how they’re mixed.
Hip-hop producers have perhaps been the biggest pioneers in this area, although some pop producers have now learnt the required skills and are applying them to more mainstream tracks. Let’s find out how it’s done.
READ: How to make fat compressed beats
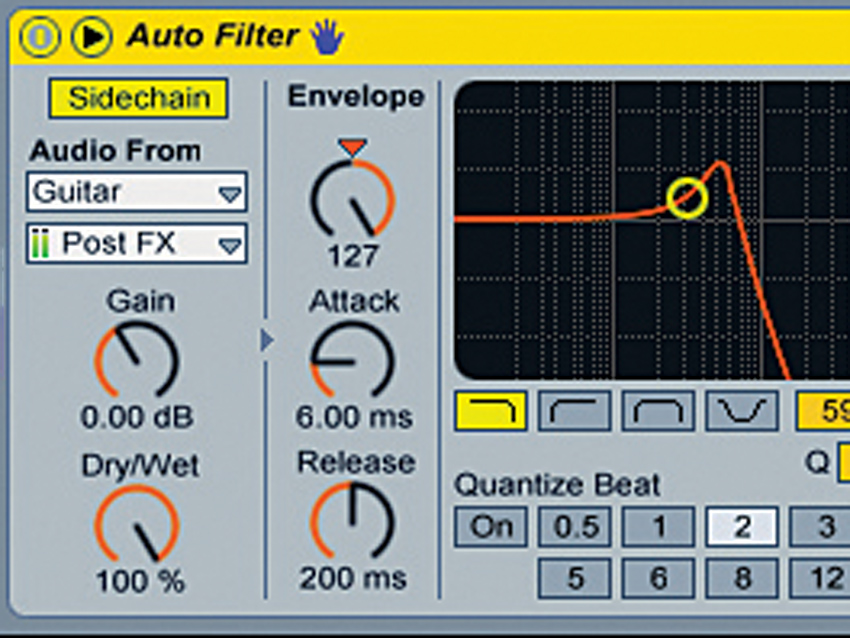
8 creative sidechaining tips
Sidechain compression is a cornerstone technique for producers in a wide range of genres, particularly dance. It's most often employed on basslines, automatically ducking the volume of the bass to let the kick drum through without muddying up the low end.
However, there's more to sidechaining than this, as these eight creative tips should prove to you.
READ: 8 creative sidechaining tips
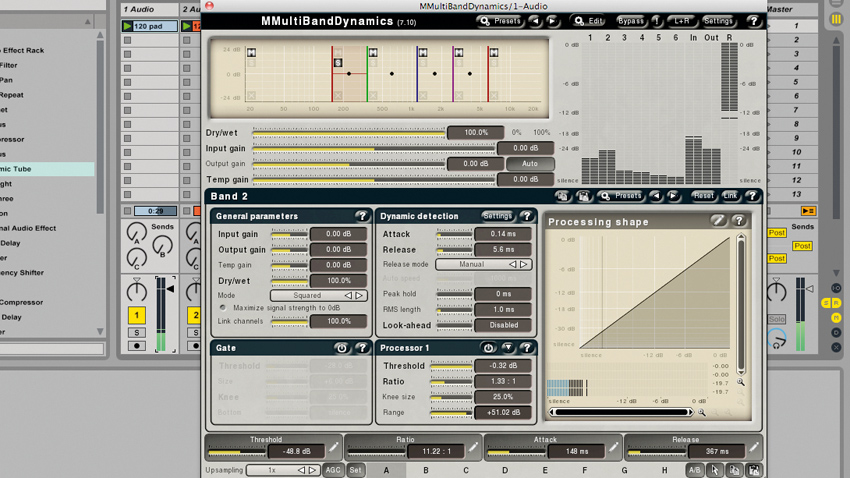
How to mix using a multiband dynamics plugin
To demonstrate the advantages of multiband processing, we'll use a specific plugin placed over a full-band pad sound.
The pad's level has been modulated with LFOs across the frequency range, causing its character to clash with some instruments. We want to reduce this movement at certain frequencies, giving our other instruments a chance to poke through the mix, but we want to leave the movement intact at other points of the frequency spectrum.
Adding a multiband dynamics plugin is the solution to this - not only can it be used like an EQ, lowering and raising levels of certain frequencies at will, but it can reduce the dynamic range of the bands it's working on at the same time, and in a completely customisable way.
We can keep the character of the pad sound poking through where we need to 'fill out' the mix, but reduce it where it detracts from the characteristics of the other instruments.
READ: How to mix using a multiband dynamics plugin
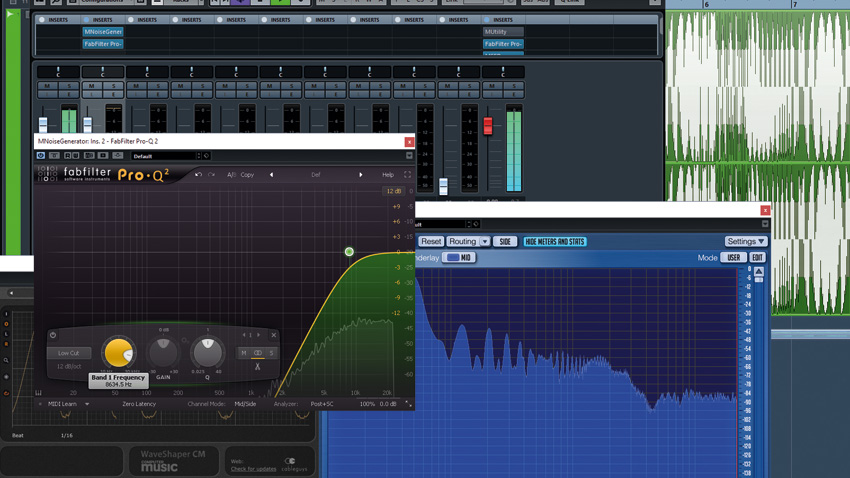
How to make your final mixdowns sound loud and clear
When it comes to the modern mixdown, loud is good - but not loud for the sake of it, and certainly not loud at the expense of class or clarity.
What happens usually? Either everything is crystal clear with no power, and it's hard to raise the overall level at the mastering stage (without destroying the delicate balance you've crafted); or, you violently compress and distort every sound and end up with a harsh, bloated, misshapen mix that somehow still sounds weak.
With the right tactics, though, there is no trade-off - you can get your mixes as loud as any commercial track without relying on some kind of mastering miracle. The genre doesn't matter - you could be producing shiny pop ballads or noisy neurofunk. It is possible to elegantly mix instruments together with clarity and competitive RMS levels.
Here, then, we'll demonstrate the fundamental principles behind getting super-loud, super-clear mixdowns. Warning: turn down your monitors, as things are about to get very loud!
READ: How to make your final mixdowns sound loud and clear
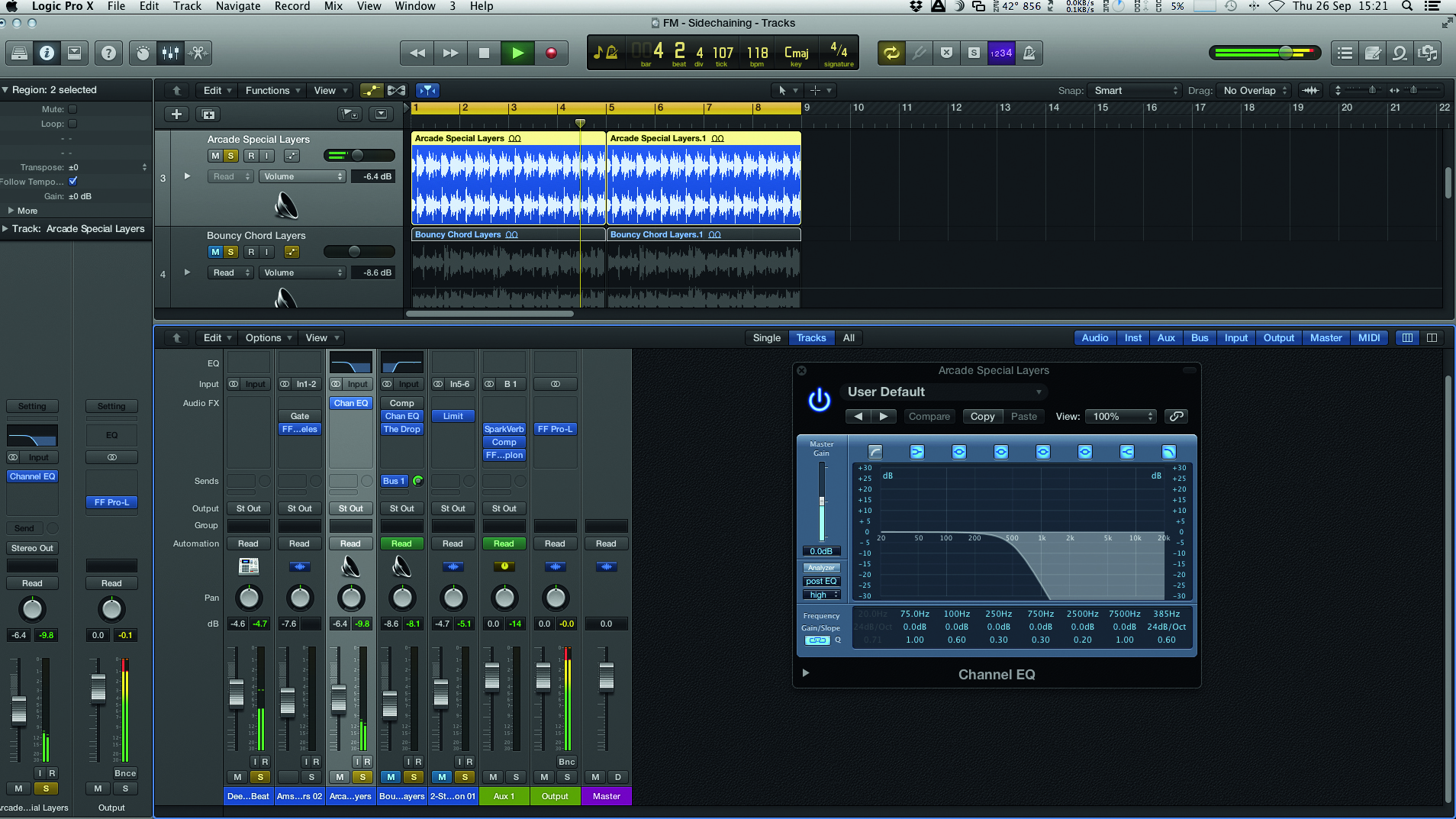
How to use rhythmic sidechain gates
When most people think of sidechaining (or ducking) it conjures up images of pumping basslines and commercial House hits. The truth is there is much more to sidechaining than simply ducking a bassline in time with your kick drum. If you trace it back to its roots you'll find the process was used more as a functional tool than a creative effect.
One example of this is de-essing. The removal of sibilance from a vocal line is now usually handled by a 'de-esser' but this is essentially a sidechain compressor with a low pass filter thrown into the mix...
READ: How to use rhythmic sidechain gates

13 ways to use sidechaining more effectively
Make the most of your sidechain-equipped dynamics plugins with this baker's dozen of indispensible tips.
READ: 13 ways to use sidechaining more effectively
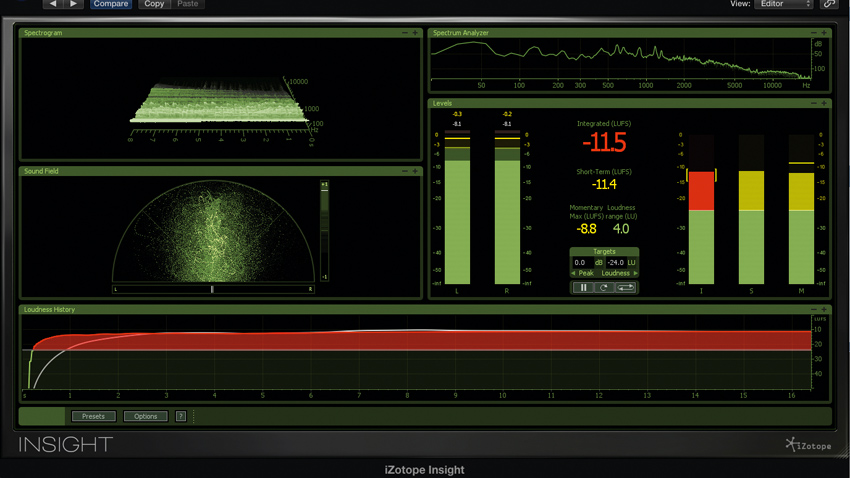
8 ways to improve your home mastering
Pro mastering services can be great. They take the guesswork out of what is sometimes perceived as a bit of a dark art. But, for reasons of convenience and cost, more and more of us are choosing to take matters into our own hands and, more often than not, this means mastering at home, in the box.
It's now totally viable to work this way, but getting the best possible results isn't necessarily easy. So, here are eight things you can try to improve your DIY mastering efforts.
READ: 8 ways to improve your home mastering
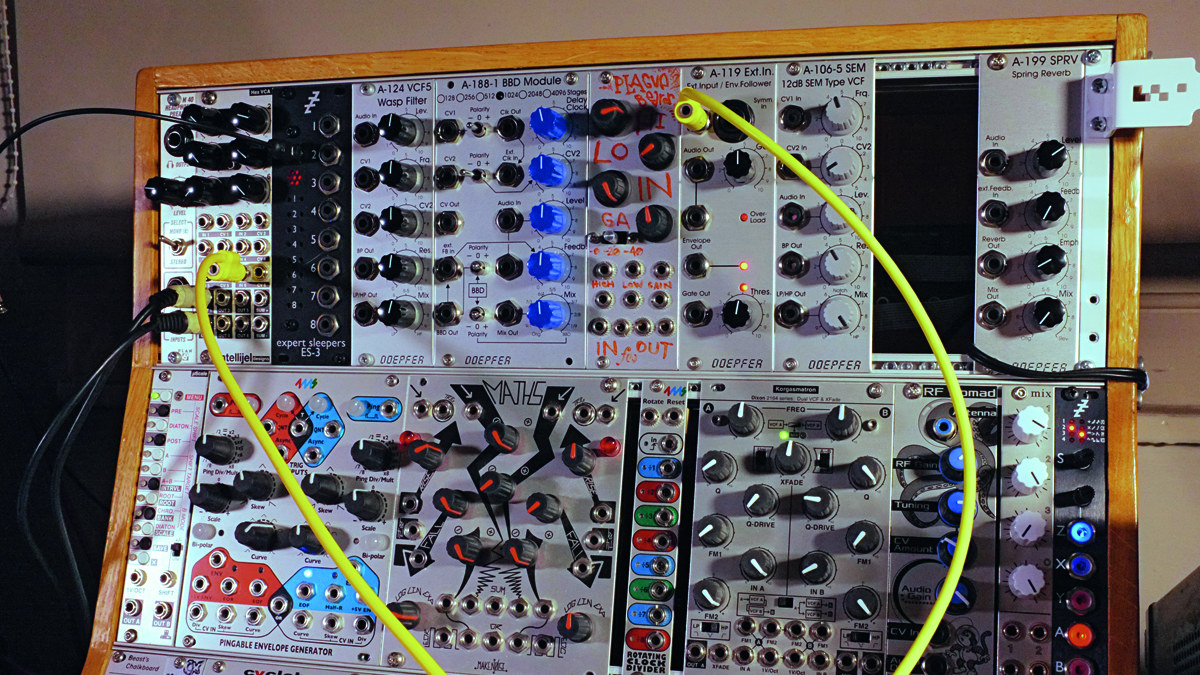

How to create a modular compressor
Nobody likes buying utilities. Utilities are boring. Right? Well, that's an easy thing to assume. When we first configure our modulars we tend to get swept up in the joy of exotic oscillators and filters and perhaps don't think to spec 'sensible' things like attenuverters, comparators, mixers or envelope followers.
As time goes on, however, the more we realise utility modules are the magic glue of modular. We could buy a 'west coast' VCO, but armed with two VCOs, a crossfade module, some VCAs and a wavefolder, we could patch one together. Sad that your oscillator doesn't have a 'fine tune' control, or octave switches? If you have a Doepfer VC polarizer or a precision adder, it does.
Make your own
Utilities unlock latent functionality in your other modules, and their usefulness compounds, until one day you realise your modular is already capable of doing something you were about to get a dedicated module in order to do.
Take compressors for example. Obviously there's an ocean off-the-shelf, and there are some excellent models in eurorack too, but let's think like we own a modular, and see if we can use 'boring' utilities to actually make one and compress a drum beat through a little patching.
And the interesting control chain we make in doing so can lead to other ideas. What if we use our compressor CV chain to modulate a BBD delay time, or drive the pitch of an oscillator, blended in with our drums? Hang on, this is starting to sound like fun!
READ: How to create a modular compressor
MusicRadar is the internet's most popular website for music-makers of all kinds, be they guitarists, drummers, keyboard players, DJs or producers.
GEAR: We help musicians find the best gear with top-ranking gear round-ups and high-quality, authoritative reviews by a wide team of highly experienced experts.
TIPS: We also provide tuition, from bite-sized tips to advanced work-outs and guidance from recognised musicians and stars.
STARS: We talk to artists and musicians about their creative processes, digging deep into the nuts and bolts of their gear and technique. We give fans an insight into the actual craft of music-making that no other music website can.
